
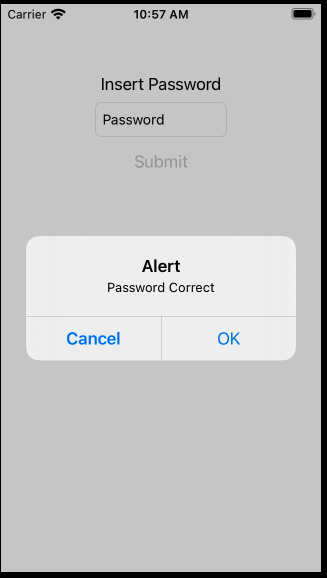
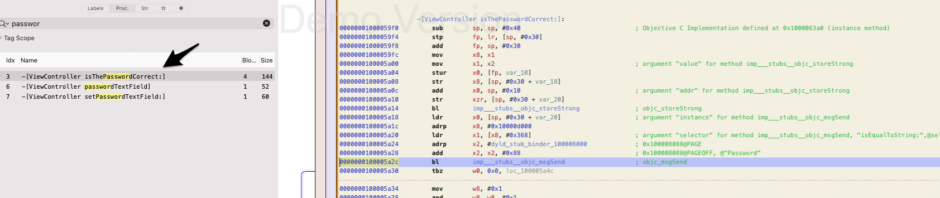
To get a better understanding of the application, the first step is to perform static analysis. We can use tools such as hopper, ghidra, etc.
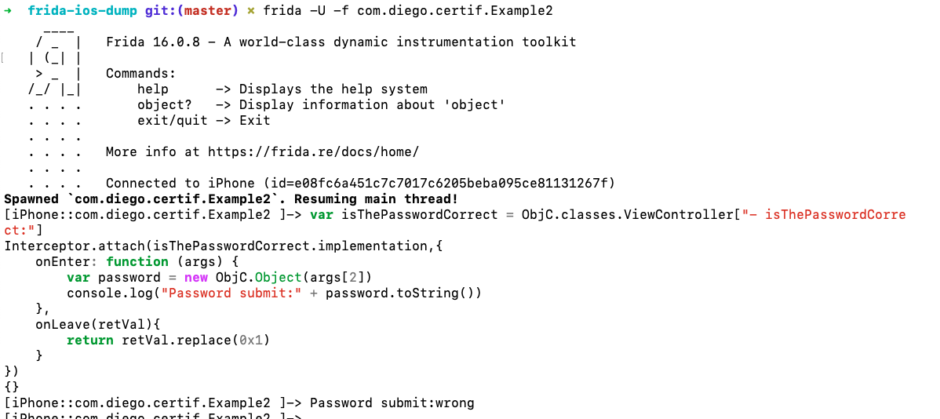
var isThePasswordCorrect = ObjC.classes.ViewController["- isThePasswordCorrect:"]
Interceptor.attach(isThePasswordCorrect.implementation,{
onEnter: function (args) {
var password = new ObjC.Object(args[2])
console.log("Password submit:" + password.toString())
},
onLeave(retVal){
return retVal.replace(0x1)
}
})
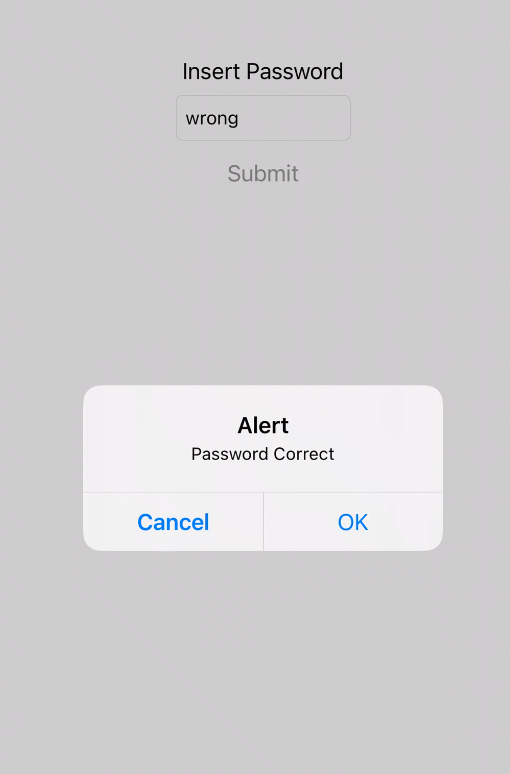
In the last script, we can only bypass the behavior of the function, but we don’t know the password yet. By examining the function isThePasswordCorrect with hopper, we can see that it uses a native Objective-C API called isEqualToString to compare two strings.
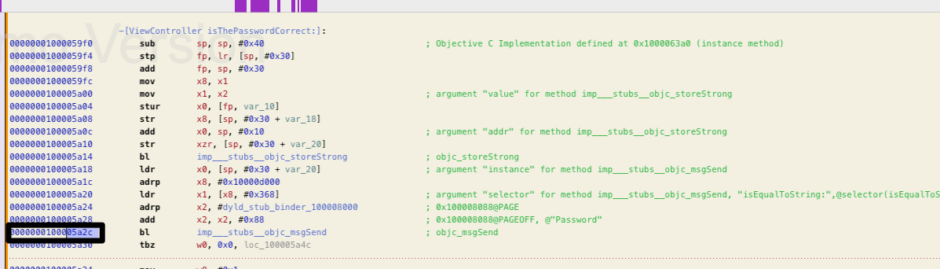
We can obtain the base address of the library in memory using Frida’s Module.getBaseAddress() function, and then we have to add the 0x05a2c offset. Next, Frida hooks and replaces the code at that particular address. Our implementation will extract the string value that contains the password.
var bin = Process.enumerateModulesSync()[0]
var targetModule = bin.name;
var addr = ptr(0x05a2c);
var moduleBase = Module.getBaseAddress(targetModule);
var targetAddress = moduleBase.add(addr);
Interceptor.attach(targetAddress, {
onEnter: function(args) {
var str = new ObjC.Object(ptr(args[2])).toString()
console.log('The Password is: ' , str);
},
});
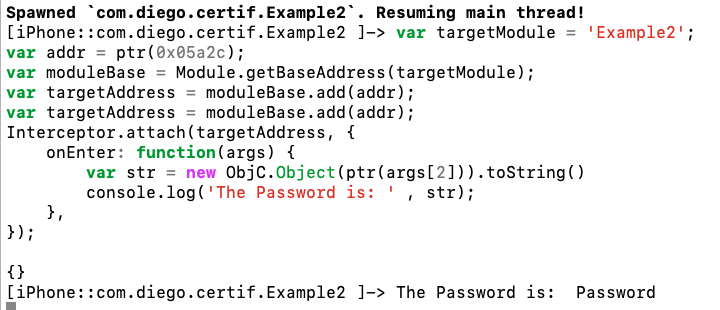
Finally, we get the “Password”
For any suggestions, or requests feel free to contact me